Ocular Myasthenia Gravis Treatment Successes And Failures
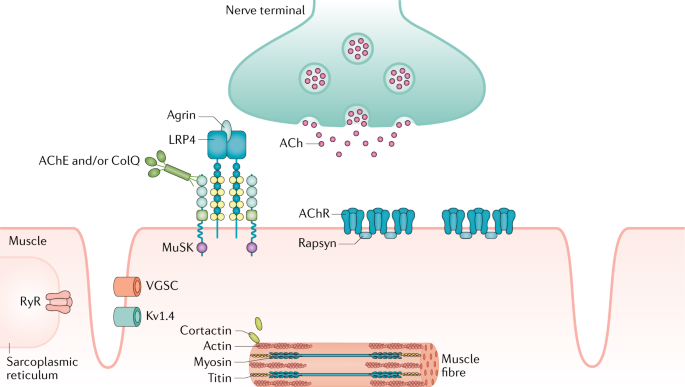
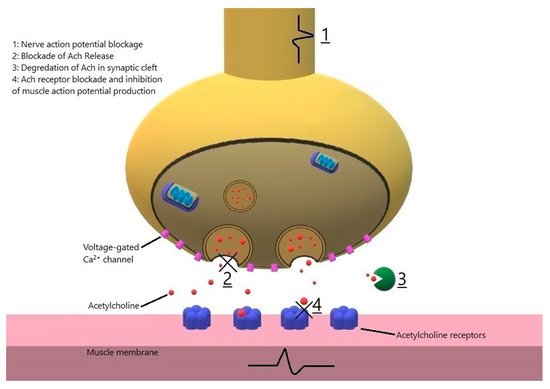
Ocular myasthenia gravis treatment successes and failures. The pathophysiologic features of myasthenia gravis are related to autoimmunity directed against the acetylcholine receptor AChR of the neuromuscular junction leading to reduced acetylcholine binding to its receptors and striated muscle weakness. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up. We previously reported that prednisone reduced the frequency of generalized myasthenia GMG and controlled.
We previously reported that prednisone reduced the frequency of generalized myasthenia GMG and controlled diplopia without major adverse effects at 2 years in patients with ocular myasthenia gravis OMG. 10 December 2008. Side effects from corticosteroids include obesity including moon face hypertension diabetes opportunistic infections osteoporosis glaucoma cataracts increased facial hair women and gastric ulcer.
Ocular myasthenia gravis. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up. The initial symptoms or.
Ocular myasthenia gravis. Patients with ocular myasthenia gravis can have disabling diplopia or functional blindness from ptosis and in most cases treatment is required. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up Mark J.
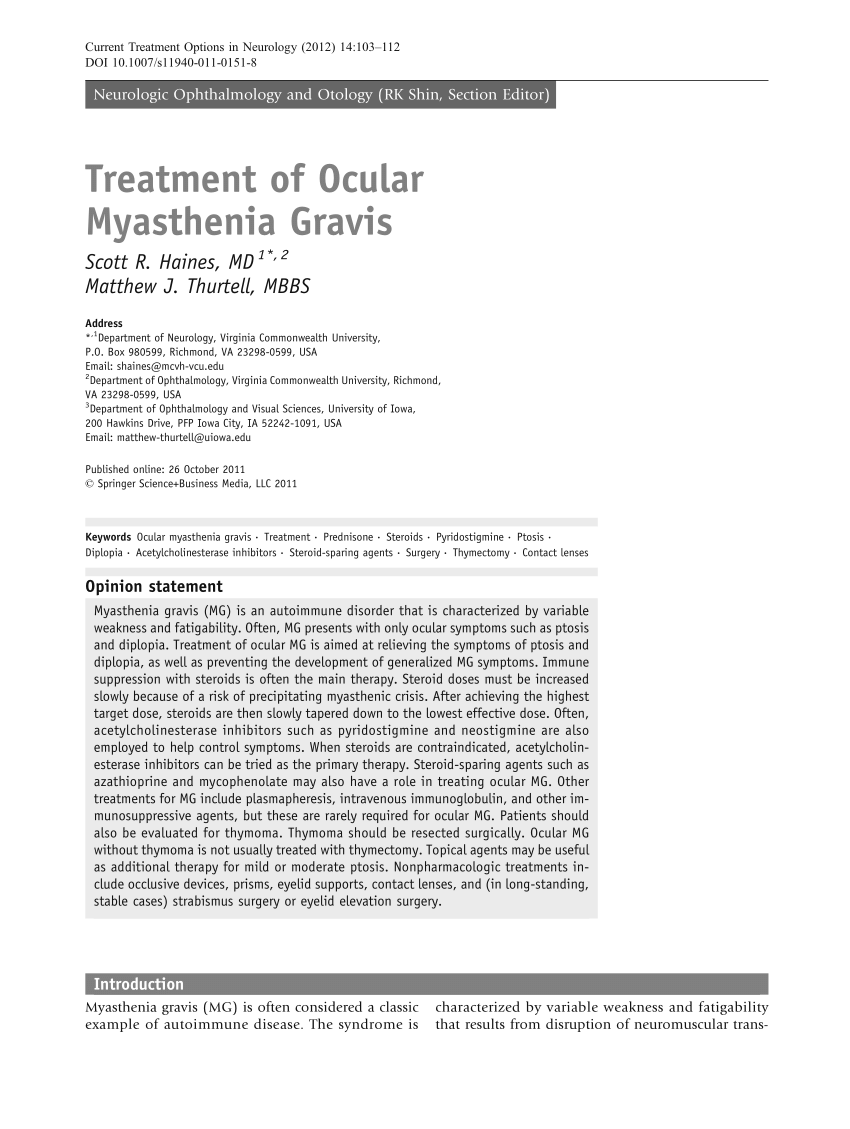
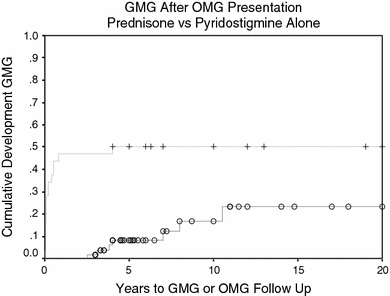
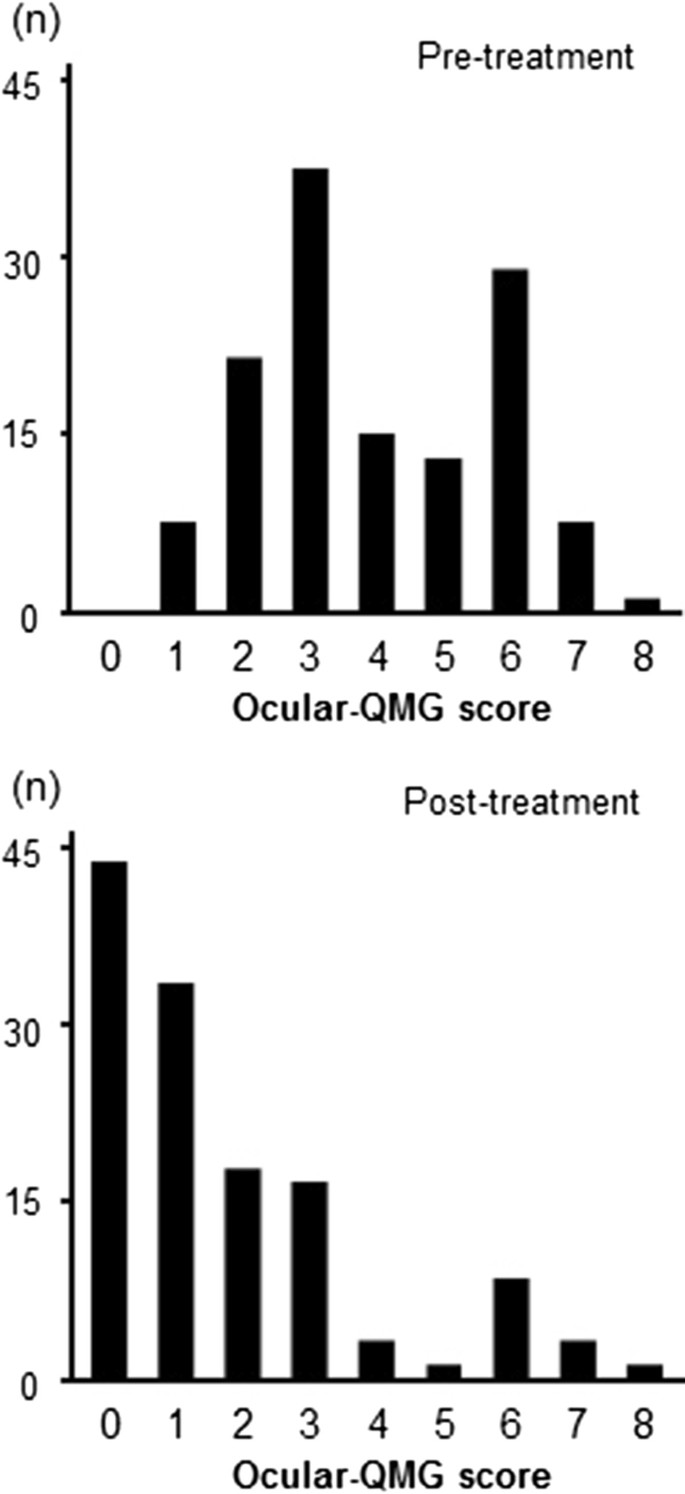
For 48 prednisone-treated patients who did not develop GMG OMG treatment failure occurred in 13. Questions remain as to whether study subjects had long-standing disease biasing results towards a steroid benefit and if prednisone merely delayed GMG onset. 89 The failure of OMG-related ptosis and diplopia to improve after corticosteroid therapy ranges from as low as 8 of 89 patients 9 in one study 10 to as.
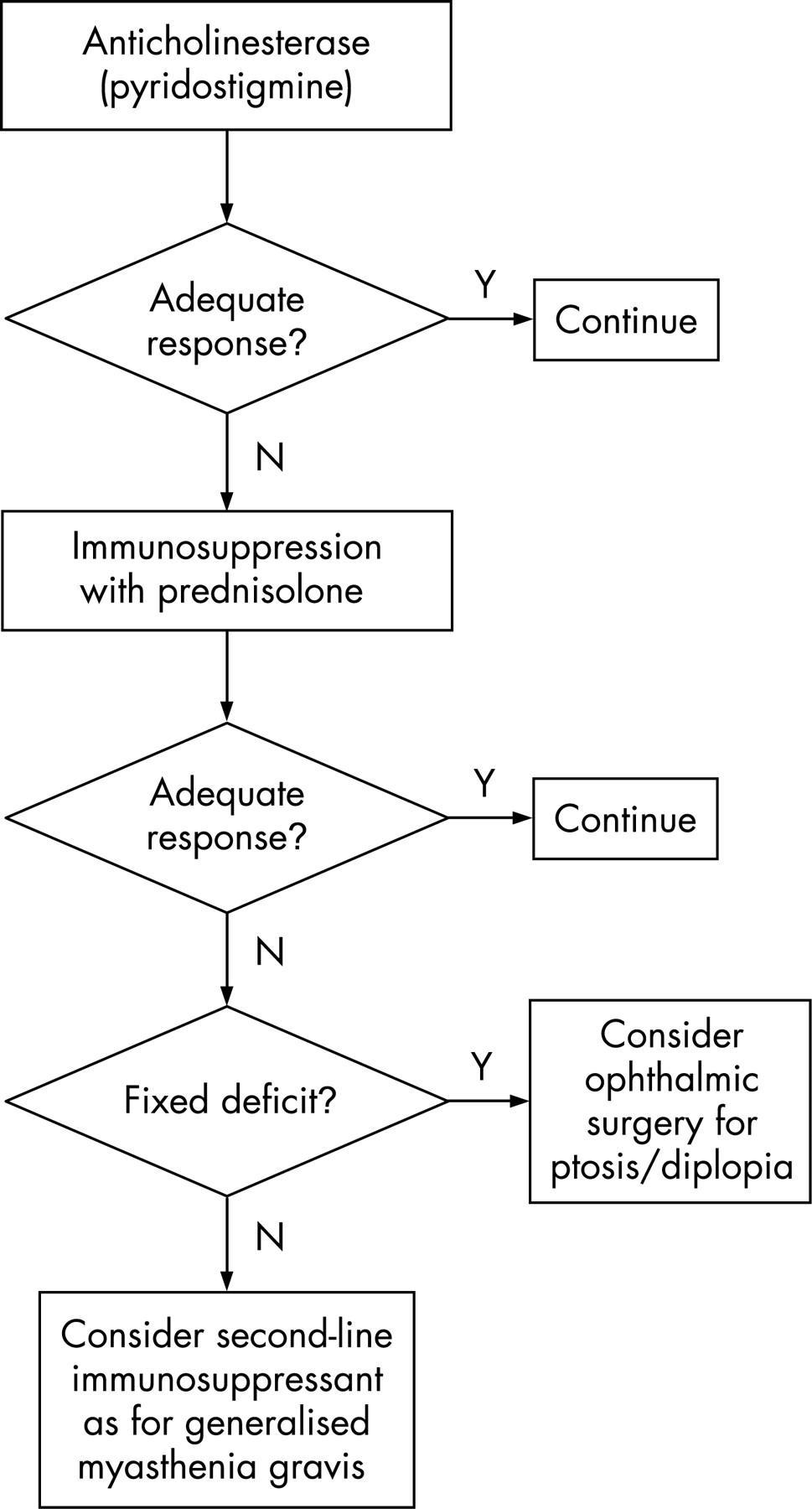
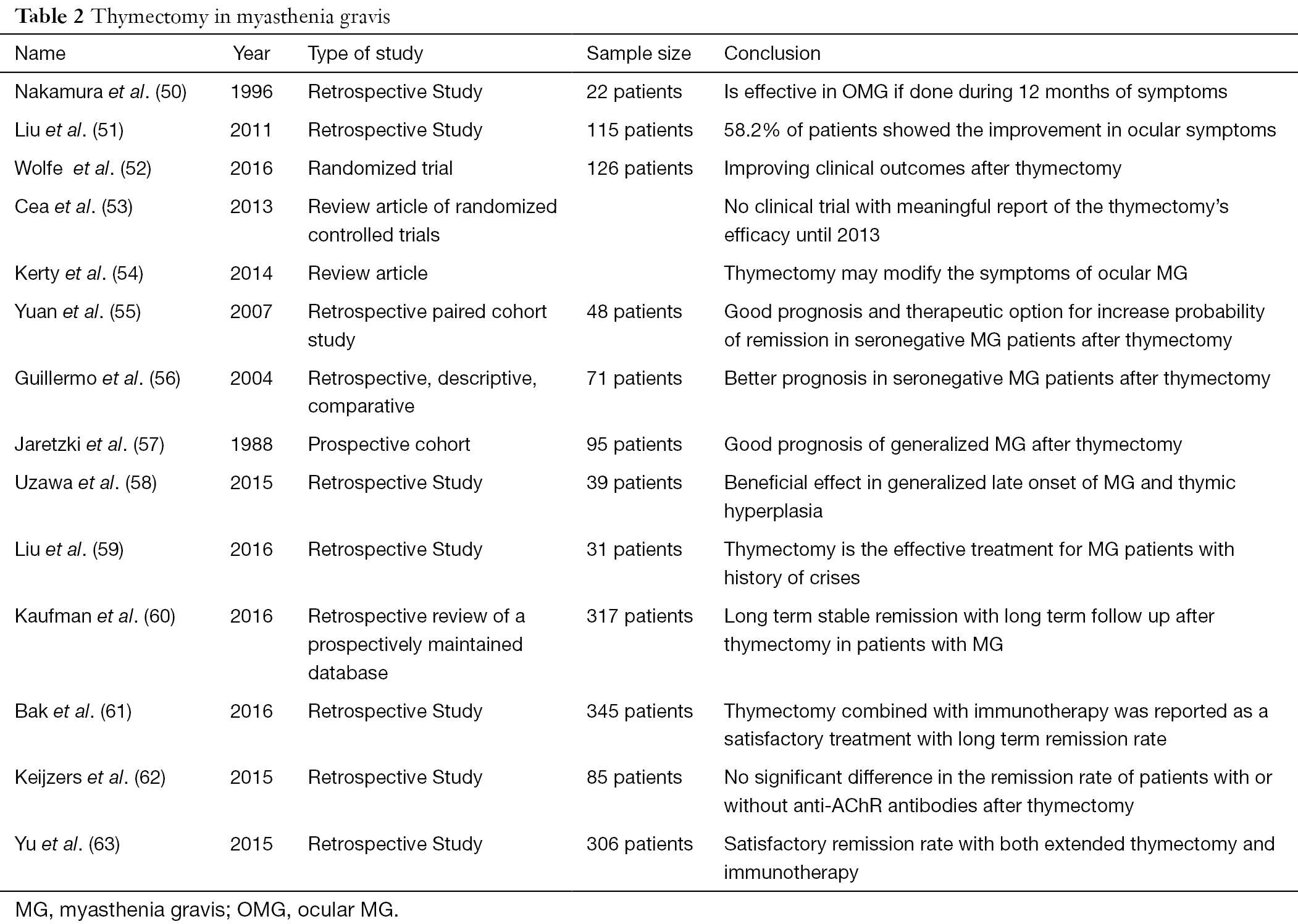
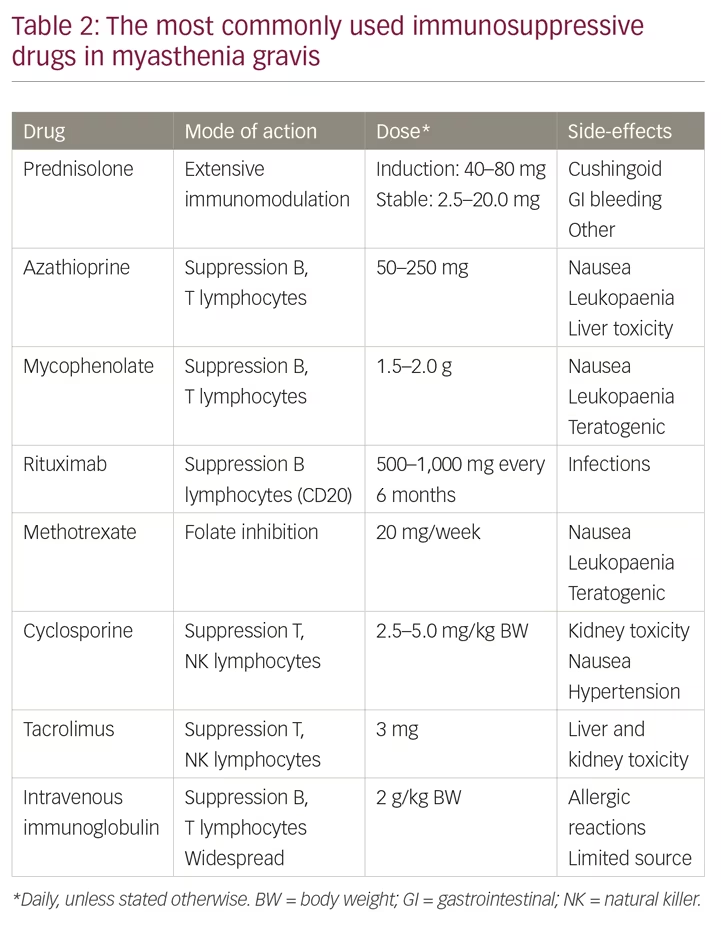
Diplopia was present at the last exam in 27 of the prednisone-treated mean 72 years and in 57 of the untreated mean 46 years OMG patients. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Like generalized myasthenia gravis there are a variety of treatments available that include pyridostigmine immunosuppression intravenous immunoglobulin plasmapheresis thymectomy lid crutches ptosis surgery and extraocular muscle surgery.
1 The initial presentation is limited to pure ocular symptoms diplopia ptosis or both in approximately 50 to 60 of cases. After OMG onset GMG developed at a mean 58 and 022 years in prednisone and untreated groups.
Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up Kupersmith Mark 2009-04-18 000000 J Neurol 2009 25613141320 DOI 101007s00415-009-5120-8 O R I G IN AL COM M UN ICAT ION Ocular myasthenia gravis.
Questions remain as to whether study subjects had long-standing disease biasing results towards a steroid benefit and if prednisone merely delayed GMG onset. The pathophysiologic features of myasthenia gravis are related to autoimmunity directed against the acetylcholine receptor AChR of the neuromuscular junction leading to reduced acetylcholine binding to its receptors and striated muscle weakness. Diplopia was present at the last exam in 27 of the prednisone-treated mean 72 years and in 57 of the untreated mean 46 years OMG patients. 89 The failure of OMG-related ptosis and diplopia to improve after corticosteroid therapy ranges from as low as 8 of 89 patients 9 in one study 10 to as. Ocular myasthenia gravis. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up Mark J. 2 Conversion rates from ocular myasthenia gravis OMG to generalized myasthenia gravis. Like generalized myasthenia gravis there are a variety of treatments available that include pyridostigmine immunosuppression intravenous immunoglobulin plasmapheresis thymectomy lid crutches ptosis surgery and extraocular muscle surgery.
Side effects from corticosteroids include obesity including moon face hypertension diabetes opportunistic infections osteoporosis glaucoma cataracts increased facial hair women and gastric ulcer. Due to the potential long-term side effects of corticosteroid therapy some experts recommend its use for the treatment of ocular myasthenia only with severe ocular disease 32. Ocular myasthenia gravis. 2 Conversion rates from ocular myasthenia gravis OMG to generalized myasthenia gravis. Ocular Myasthenia Gravis Treatment. The pathophysiologic features of myasthenia gravis are related to autoimmunity directed against the acetylcholine receptor AChR of the neuromuscular junction leading to reduced acetylcholine binding to its receptors and striated muscle weakness. Treatment successes and failures in patients with long-term follow-up.














/myasthenia-gravis-2860863_v1-01-9d4796e780844adf973d3ca973528994.png)


















Post a Comment for "Ocular Myasthenia Gravis Treatment Successes And Failures"